Why Brands Are Betting on AI-Generated Influencers
From cost savings to creative freedom, virtual influencers are redefining brand engagement across the globe.
As someone who has experienced both the highs and lows of working with influencers, I’ve developed a bit of a love/hate relationship with them. On one hand, we’ve seen tremendous success partnering with some truly talented influencers who’ve helped our clients connect with audiences in authentic and impactful ways. On the other hand, we’ve also dealt with the headaches of wrangling difficult and undisciplined influencers—many of whom have become emboldened by making too much money too soon for doing too little. It’s no wonder, then, that the idea of a new kind of influencer—one that’s fully obedient and always on-message—might seem appealing.
Enter virtual influencers: AI-generated digital personas that are beginning to carve out a significant space in the marketing landscape. These influencers are attractive to brands not just for their creative possibilities but also for their predictability and control.
Yet, like many others, I can’t shake a sense of dread about Artificial Intelligence taking over everything, including the influencer space. These new, soulless influencers offer a solution to the unpredictability of human behavior, but they also represent a step toward a more impersonal, AI-driven future. Are they the answer to the challenges of influencer marketing, or are they simply another sign of technology encroaching on human-driven spaces?
AI-generated influencers are reshaping consumer engagement and brands around the globe are betting big on these digital characters. But their emergence isn’t without its complexities and ethical considerations.
The Emergence of Virtual Influencers
Virtual influencers are digital characters created using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer-Generated Images (CGI), designed to engage audiences on social media just like human influencers—but with one key difference: they are entirely fictional. Unlike traditional influencers, virtual influencers are controlled entirely by their creators, allowing brands to tailor every aspect of their behavior, appearance, and messaging.
This has sparked a new wave in the influencer marketing world, where control and consistency are paramount.
The concept isn’t entirely new; virtual personas have existed in various forms for some time. However, the past few years have seen a significant surge in their popularity and sophistication. Take Lil Miquela, for example—one of the most well-known virtual influencers with over 2,5 million Instagram followers. Created by the Los Angeles-based company Brud, Lil Miquela has collaborated with major brands like Calvin Klein, Prada, and Samsung, blurring the lines between virtual and real-world celebrity.
Similarly, Shudu, the world’s first digital supermodel, has worked with luxury brands such as Balmain and Ellesse, capturing the imaginations of fashion followers worldwide.
The rise of virtual influencers is not just a Western phenomenon. In Japan, Imma, a virtual model with a strikingly realistic appearance and over 400,000 followers, has partnered with brands like IKEA to promote their furniture in a futuristic home setting.
In South Korea, Rozy, a virtual influencer created by Sidus Studio X, has become a sensation, working with brands such as Shinhan Life Insurance and Hyundai to connect with tech-savvy audiences in innovative ways. These examples highlight a global trend: virtual influencers are becoming a viable—and sometimes preferable—alternative to their human counterparts.
The market potential is substantial. Valued at $4.6 billion in 2022, the virtual influencer market is projected to reach $16.2 billion by 2030. This growth is driven by several factors: the demand for consistent and controllable brand messaging, the appeal to tech-savvy younger audiences, and the overall novelty that virtual influencers bring to the table.
Unlike human influencers, who can be unpredictable or require significant management, virtual influencers offer brands the ability to maintain complete control, all while tapping into the same engagement-driven benefits that make influencer marketing so powerful.
However, their emergence does beg a few questions. As these AI-generated personas continue to gain popularity, will brands be able to navigate the complexities of authenticity and consumer trust? Despite their appeal, virtual influencers also raise ethical considerations about the authenticity of engagement and the potential for misleading audiences. As we move forward, will brands meet the challenge of balancing the convenience and creativity of virtual influencers with the values of transparency and authenticity that consumers increasingly demand?

Why Brands are Turning to Virtual Influencers
Virtual influencers offer brands the ultimate control over their messaging and persona, making them an attractive option for companies seeking consistent branding. Unlike human influencers, whose behavior can sometimes be unpredictable or off-brand, virtual influencers are entirely scripted, ensuring that every post aligns perfectly with the brand’s image and values. This level of control helps brands maintain a consistent voice across campaigns, reducing the risk of PR missteps or influencer scandals.
The appeal of virtual influencers is also evident in consumer engagement. According to recent data, 60% of consumers have interacted with a virtual influencer, and 35% have made a purchase based on those interactions. This demonstrates the growing effectiveness of virtual influencers in driving consumer actions, comparable to, if not exceeding, traditional influencers in some cases.
For example, fried chicken fast-food chain KFC was an early adopter of this technology when it reimagined its iconic Colonel Sanders character as a CGI influencer in the U.S. This synthetic version of the Colonel was transformed into a suave, digitally-crafted character who engages with audiences on Instagram. This modern take on the Colonel not only helped refresh KFC’s brand image but also allowed the company to precisely control the character’s messaging and interactions, ensuring every post was on-brand and aligned with its marketing objectives. By doing so, KFC tapped into the influencer trend while avoiding the unpredictability often associated with human influencers.
Similarly, in Brazil, the virtual influencer Lu do Magalu, created by retail giant Magazine Luiza, has become one of the most followed virtual influencers globally, with over 14 million Instagram followers. Lu is used to promote everything from electronics to home goods, all while embodying the brand’s friendly and approachable persona. This consistent and controlled presence helps maintain brand messaging across diverse product categories, making Lu a reliable ambassador for the company.
Additionally, virtual influencers offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional influencer partnerships. Brands can save on expenses like travel, accommodations, and talent fees, which can quickly add up with human influencers. In markets where digital engagement is rising rapidly, such as Southeast Asia, virtual influencers provide an efficient and scalable solution for reaching large audiences without the logistical challenges of coordinating with multiple human influencers.
This blend of consistent branding, high engagement, and cost-effectiveness is why many brands are turning to virtual influencers as a key component of their marketing strategies, leveraging the digital realm to connect with audiences in new and innovative ways.
The Appeal to Target Audiences
Virtual influencers have a strong appeal to Gen Z and digital natives—groups that are highly tech-savvy and deeply immersed in digital interactions. These younger audiences are often more receptive to AI-driven personas, finding them fresh, innovative, and closely aligned with their digital-first lifestyles. This makes virtual influencers an increasingly attractive tool for brands aiming to connect with this demographic.
Statistics show that 55% of Gen Z consumers prefer virtual influencers over human influencers for product recommendations. This preference reflects a growing comfort and intrigue with AI-generated personas, as they offer new and engaging experiences that stand out in crowded digital spaces.
One notable example is Prada’s collaboration with Candy, a virtual influencer who was developed to embody the playful and bold characteristics of their Prada Candy fragrance line. This partnership effectively captured the attention of younger audiences worldwide by blending high fashion with digital innovation, creating a buzz that resonated well with Gen Z and millennials.
In South Korea, Rozy, a virtual influencer created by Sidus Studio X, has become a sensation, amassing millions of followers. Rozy’s relatable yet aspirational content has led her to work with several major brands, including Shinhan Life Insurance, highlighting how virtual influencers can seamlessly integrate into various cultural contexts while appealing to younger, tech-savvy consumers.
Any Malu, a Brazilian virtual influencer known for her humorous and relatable content, has collaborated with several local brands, including famous flip-flop maker, Havaianas, to connect with younger audiences through playful and engaging digital content.
Engagement metrics further support the effectiveness of virtual influencers. Data shows that these digital personas often achieve engagement rates up to three times higher than their human counterparts, largely due to their novelty and the highly controlled, polished content they can deliver. This capability allows brands to precisely tailor virtual influencers’ personas and interactions to align with audience preferences, avoiding the unpredictability of human behavior.
This strong appeal to digital natives, coupled with impressive engagement rates and the ability to adapt across different markets, makes virtual influencers a powerful asset for brands targeting younger audiences. As the trend continues to grow, brands are likely to increasingly incorporate virtual influencers into their strategies, leveraging their unique ability to connect with Gen Z in authentic and innovative ways.
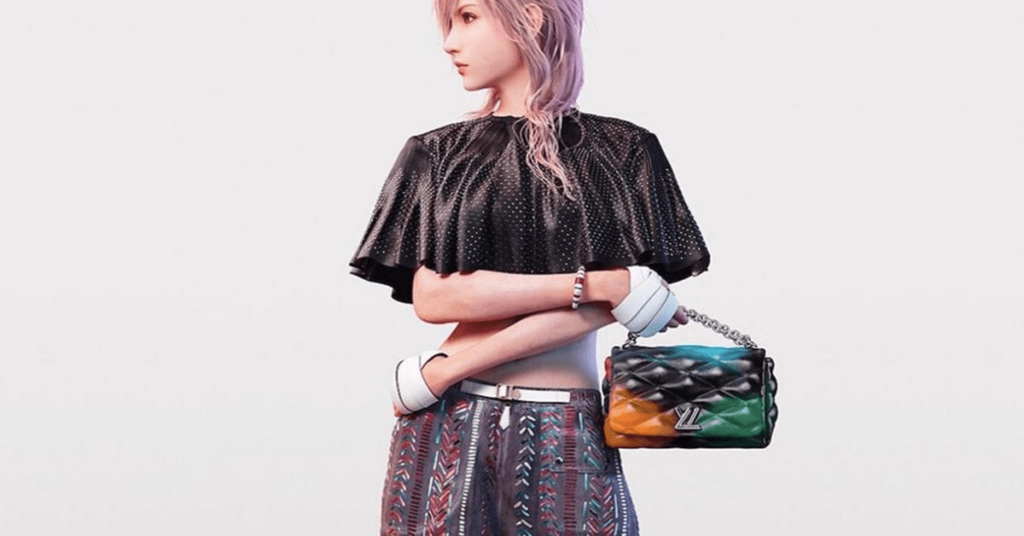

Creative Flexibility and Innovation
One of the most compelling advantages of virtual influencers is the limitless creative opportunity they present. Unlike human influencers, virtual personas can be placed in any setting or scenario, unbound by the physical limitations that come with working with real people. This allows brands to push creative boundaries and craft unique narratives that stand out in the crowded digital space.
In China, virtual idol Luo Tianyi has exemplified this creative potential. Luo Tianyi, a digital pop star with a massive following, has collaborated with global brands like L’Oréal and Procter & Gamble, integrating local cultural elements into her appearances to resonate with Chinese audiences. These collaborations have allowed brands to connect with younger consumers in ways that feel fresh and culturally relevant, leveraging Luo Tianyi’s digital persona to seamlessly blend product promotion with entertainment.
Rae, a virtual influencer created by CapitaLand in Singapore, promotes retail and lifestyle experiences across CapitaLand’s properties. Rae engages with audiences through interactive social media posts and virtual tours, blending real estate marketing with lifestyle content in innovative ways.
Brands also see a measurable impact from using virtual influencers. Studies have shown that campaigns featuring virtual influencers can see a 10-20% increase in social media engagement compared to those using traditional influencers. This enhanced engagement is driven by the novelty of virtual influencers and the flexibility they offer in creating visually striking, imaginative content that captures audience attention.
A notable example of creative crossover is Louis Vuitton’s use of Lightning, a character from the popular video game series Final Fantasy. By incorporating Lightning into their advertising campaigns, Louis Vuitton was able to fuse high fashion with digital culture, creating a unique and memorable campaign that appealed to both fashion enthusiasts and gaming fans. This innovative approach showcases the potential of virtual influencers to create unexpected and engaging brand experiences that resonate across different interests and demographics.
The ability to explore creative avenues without the constraints of reality gives virtual influencers a distinct edge, making them a powerful tool for brands looking to innovate in their marketing strategies. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of virtual influencers in pushing creative boundaries is likely to expand, offering brands new ways to captivate and connect with audiences.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While virtual influencers offer numerous advantages, they also present significant challenges, particularly around issues of authenticity and trust. As AI-generated personas become more prevalent, global concerns have emerged about the authenticity of these digital characters. A survey found that 42% of consumers express skepticism about virtual influencers, questioning their ability to provide genuine recommendations or represent real human experiences. This skepticism highlights a critical hurdle for brands: maintaining consumer trust in an era where the line between reality and fiction is increasingly blurred.
The ethical implications of virtual influencers extend beyond mere skepticism. As these digital personas are entirely crafted by brands or agencies, there’s an inherent risk of misleading marketing and the potential to exploit audiences by presenting fictional narratives as real. This blurring of reality and fiction can lead to a loss of transparency, where consumers might feel deceived by content that masquerades as authentic but is, in fact, meticulously staged.
A notable example of these ethical challenges occurred when Calvin Klein featured Lil Miquela, a popular virtual influencer, in an ad alongside supermodel Bella Hadid. The ad depicted the two characters in an intimate scene, which sparked controversy and backlash for what many perceived as the exploitation of LGBTQ+ themes to garner attention without genuine representation. The incident highlighted the delicate balance brands must strike when using virtual influencers in campaigns, especially when addressing sensitive social issues.
Similarly, in Saudi Arabia, the CGI influencer Rania was criticized for not accurately reflecting the diversity and complexity of Saudi society, raising questions about the responsibility of brands when creating and promoting virtual characters that represent real cultural identities.
Globally, about 30% of consumers report feeling uncomfortable with virtual influencers, underscoring the need for brands to navigate this space thoughtfully. Brands must ensure that their use of virtual influencers does not come across as inauthentic or manipulative. Transparency about the nature of these digital personas and clear communication regarding their purpose can help mitigate some of these concerns.
As virtual influencers continue to evolve, brands will need to carefully consider the ethical ramifications of their use, balancing the innovative potential of these digital characters with the imperative to maintain trust and authenticity in their marketing strategies. Navigating this space requires a nuanced approach that respects consumer expectations and fosters genuine connections, even in a virtual landscape.
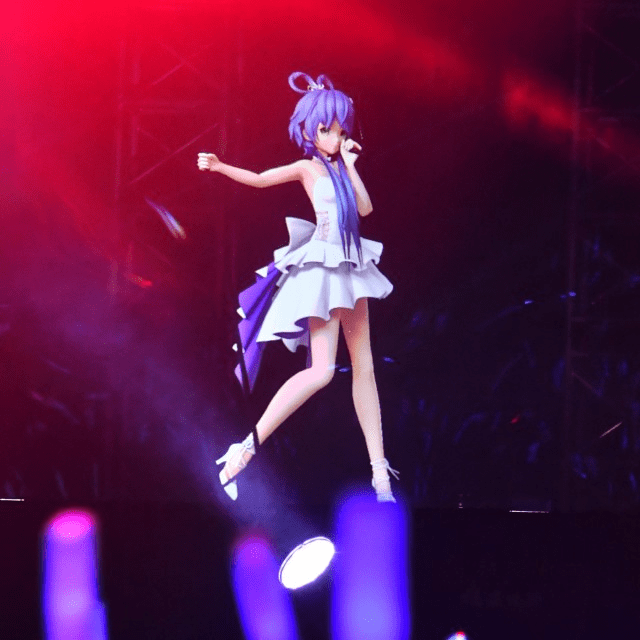

Is This the Future of Influencer Marketing?
As brands continue to explore the potential of virtual influencers, it’s clear that these AI-driven personas are more than just a passing fad. Virtual influencers are set to grow, particularly in regions with high digital penetration like the Middle East and Asia, where the appetite for innovative, tech-savvy marketing solutions is strong. In these regions, digital engagement is not just prevalent; it’s a cultural norm, making virtual influencers a natural fit for connecting with audiences that are increasingly comfortable interacting in digital spaces.
The future of virtual influencers lies in their ability to integrate even more deeply with AI technologies. As AI capabilities advance, virtual influencers will likely evolve beyond static, pre-scripted characters into more dynamic and interactive personas. This could include using AI to generate personalized content based on user preferences, behaviors, or even real-time interactions, creating a more engaging and customized experience for each follower. This level of personalization could significantly enhance global engagement, making virtual influencers not just a marketing tool, but a highly adaptive component of brand strategy.
Projections indicate that investment in virtual influencers will continue to rise. By 2025, it’s estimated that 10% of influencer marketing budgets will be allocated to virtual influencers worldwide. This shift reflects the growing confidence brands have in the effectiveness of virtual influencers to deliver consistent, innovative, and impactful marketing results. The appeal of virtual influencers—driven by their creative flexibility, control over messaging, and the ability to seamlessly blend into various digital environments—positions them as a key element in the future of influencer marketing.
However, this doesn’t mean that real live influencers are going away. Far from it. Human influencers bring a level of authenticity, relatability, and emotional connection that virtual influencers, despite their advancements, may never fully replicate. The unique ability of human influencers to build genuine relationships, share personal stories, and connect on a deeper level with their audiences remains irreplaceable. But for brands to fully leverage the strengths of real influencers, there will need to be a greater emphasis on control and strategic alignment. This is where agencies like ROSE come in, offering expertise in integrating influencers into campaigns that adhere to strategic goals, ensuring that the messaging aligns with the brand’s vision rather than allowing influencers to just do their own thing. By doing so, brands can still maintain the authenticity that human influencers bring to the table while exerting the necessary control to meet their marketing objectives.
As virtual influencers become more sophisticated, brands must remain vigilant about maintaining authenticity and trust with their audiences. The challenge will be to leverage the technological advantages of virtual influencers without losing the human touch that makes influencer marketing so powerful. Balancing these elements will be critical in determining whether virtual influencers can truly shape the future of this dynamic field.
Final Thoughts
As the landscape of influencer marketing continues to evolve, brands have an opportunity to strategically integrate both virtual and human influencers into their campaigns across different markets. By leveraging the strengths of virtual influencers—such as creative flexibility, control over messaging, and the ability to seamlessly operate in digital environments—brands can reach audiences in innovative ways that were previously unimaginable. At the same time, real influencers offer irreplaceable authenticity, relatability, and emotional connection that resonate deeply with consumers.
To maximize the potential of both types of influencers, brands must strike a careful balance, ensuring that their strategies align with their overarching goals while maintaining the trust and engagement of their audiences.
Looking ahead, as technology continues to advance, virtual influencers are likely to become a staple in global marketing strategies, offering brands unique and personalized ways to connect with diverse audiences. The future of influencer marketing is not about choosing between virtual and human influencers, but rather about finding the right mix that enhances brand storytelling and drives meaningful engagement.



